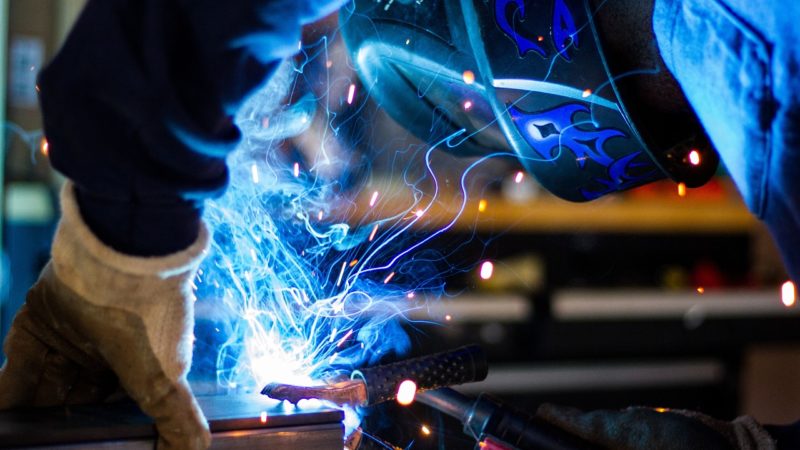
Welders repair, assemble and fabricate metal structures through the use of measuring tools, shapers, and cutters. They are employed in a variety of industries such as construction, shipbuilding, automobile manufacturing, railroad manufacturing, pipeline transportation, natural gas distribution, paperboard manufacturing, and electrical power generation.
What Does a Welder Do?
Welders are responsible for carrying out a number of tasks such as:
- Joining metal parts in overhead, vertical, or flat positions
- Studying, interpreting, and analyzing material safety data, sketches, blueprints, and engineering drawings
- Calculating the dimensions of metal parts and materials that have to be welded
- Assessing components, structures, and welded surfaces to identify errors
- Carrying out routine inspections for leaks and cracks
- Applying and mixing protective coatings
Working Conditions and Timings
Welders can work outdoors or indoors, depending upon the industry that they are employed in. They work full-time; some even have to work overtime to complete time sensitive construction projects. Thus, welding jobs can be exhausting and physically draining.
Why You Should Become a Welder?
There are many reasons as why you should consider pursuing a career in this field. First and foremost, this career is in high demand and promises lucrative salaries. Second, you don’t need a university degree to become a welder. All you need is professional on-the-job training, along with vocational training. Thus, you don’t need to worry about college loans and can start working right after completing a vocational course.
Third, this career can give you tons of exposure as you will have the opportunity to work in diverse industries. If you are passionate about flying, you can find employment in the aerospace industry, and if you enjoy working outside instead of working in confined indoor spaces, then you can choose to find employment in the pipeline welding or construction industry.
Types of Welders
The details regarding different types of welders are mentioned below:
- Industrial Pipeline Welders: These welders use a range of welding techniques to maintain and install pipelines. Industrial pipeline welders have to work long days and are often exposed to extreme weather conditions.
- Underwater Welders: This type of welding involves repairing, maintaining, and installing rigs and pipelines. These welders have to go underwater in order to weld. There is a lot of risks involved in underwater welding because the welders are exposed to dangerous working conditions such as high water currents, unfavorable temperatures, and darkness. Thus, these welders are required to obtain a diving certification along with welding certifications.
- Military Support Welders: Since the US military has equipment and bases all over the world, there is a constant need for repair and maintenance of ships, vehicles, and equipment. Thus, military support welders are in high demand. However, since these welders have to work on-site, they have to spend a lot of time away from their families.
- Nuclear Industry Welders: Nuclear Industry Welders probably have to face the most dangerous working conditions out of all types of welders because they may be exposed to dangerous radiation. They have to clear many tests and obtain several certifications in order to pursue careers in this field.
- Aerospace Welders: Aerospace welders work on equipment and machinery found in space shuttles, airplanes, and their supporting structures. This may require working with metals like aluminum, stainless steel, and carbon steel.
How to Become a Welder?
In order to establish a career in welding, one does not need a formal university education. However, a specific skill set is required which can be gained by completing a vocational training course. Currently, there are many schools in the US, such as the Apex Technical School, Ohio Technical College, Owens Community College, Hobart Institute of Welding Technology, and Manhattan Tech, that are offering welding programs.
Students can enroll in a Welding Technology Certificate program that requires completion of around 42 credit hours or an Associate of Applied Science (AAS) in Welding Technology that requires completion of 63 credit hours. The curriculum of these programs is composed of a range of modules such as Welding Safety, Cutting Processes, Blueprint Reading and Fabrication, Welding Metallurgy, Flux Cored ARC Welding, and Welding Project Management.
Requirements to Become a Welder
The following requirements have to be met in order to become a welder. The individual:
- Must possess a high school diploma or an equivalent educational qualification
- Must have received vocational training
- Must have excellent knowledge about welding tools, machinery, and manual/mechanical welding techniques
- Should have the ability to interpret and read engineering drawings and blueprints
- Should have good mathematical, analytical, project management, and administrative skills
- Should be detail-oriented since welding jobs require material inspection, identification of errors, and strict adherence to safety standards
- Should be physically fit because welding jobs can be exhausting and physically draining
- Must be comfortable with learning about new technology
Career Outlook for Welders
Employment data taken from the US Bureau of Labor Statistics indicates that Welders, Cutters, Solderers, and Brazers made an hourly median pay of $19.89 and annual median pay of $41,380. The number of people employed in this field in 2018 was 424,700. It is estimated that the job opportunities for these professionals will increase by 3% from 2018 to 2028, which will create 14,500 more jobs.